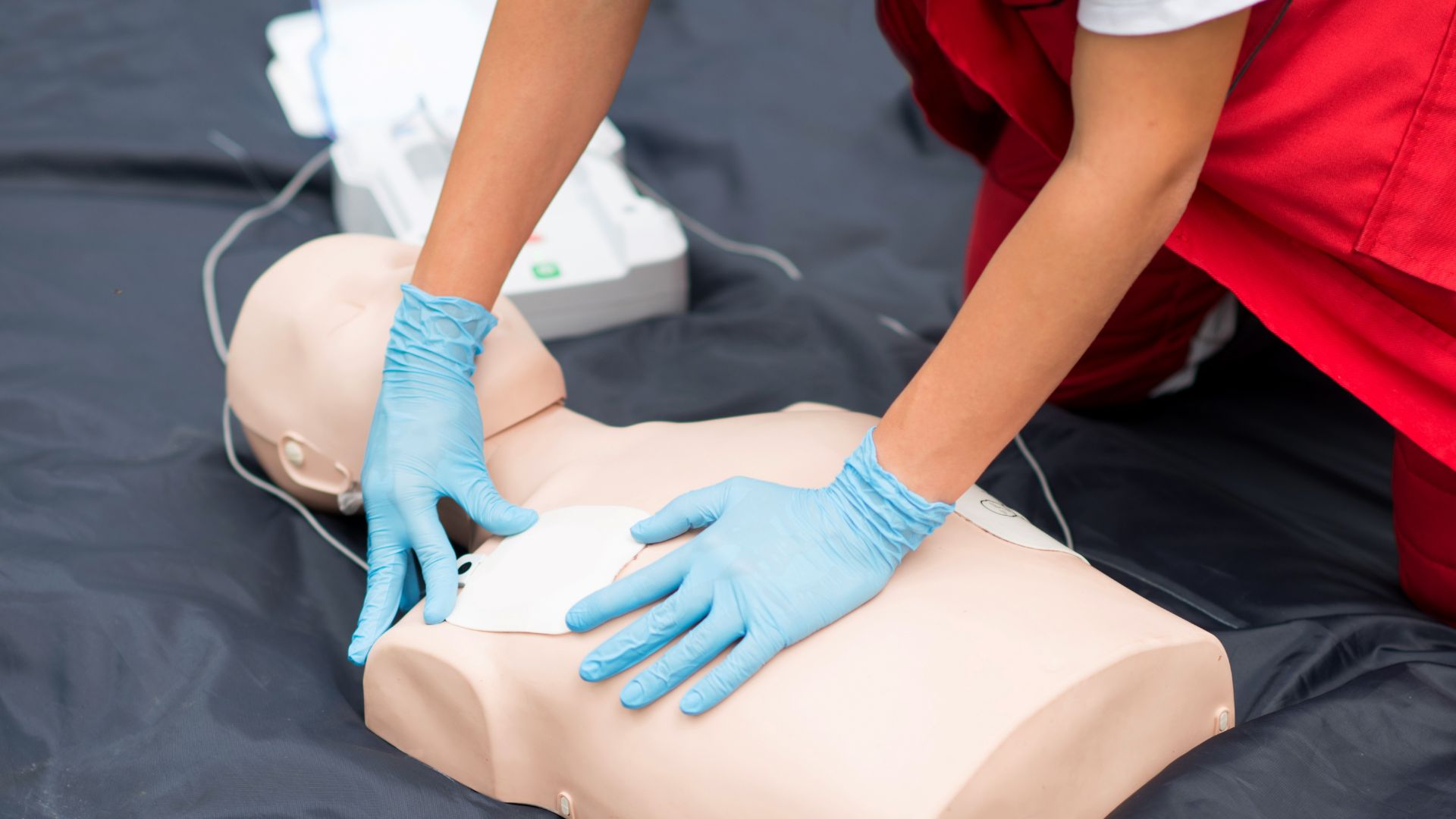
CPR techniques are essential life-saving abilities that may be crucial when every second counts. When someone is experiencing a cardiac arrest, CPR can drastically increase the likelihood of survival. Staying up to speed on the latest CPR standards ensures your knowledge and skills are up-to-date, effective, and per the latest practices.
The recommendations and methods for CPR have changed over the years as medical knowledge and research do.. Healthcare professionals and the general public must follow the most recent CPR recommendations to achieve the best results in life-threatening situations.
Keep reading to learn more about CPR Techniques and how to stay updated on the latest guidelines.
Why Following The CPR Guidelines Is So Important?
Following these guidelines means ensuring effective and standardized care during cardiac emergencies. These guidelines were created using results from in-depth studies, reliable data, and insight from medical professionals. Following CPR guidelines is crucial for many reasons.
Maximizing Chances of Survival
CPR guidelines are created to maximize a person’s probability of surviving a cardiac arrest. They describe the most efficient ways to keep blood flowing and oxygenated until the arrival of advanced medical assistance. This means correct positioning of the body, giving chest compressions, and use of AED.
Consistency and Uniformity
This ensures that the quality of CPR is maintained across different settings, enabling seamless transitions in care and improving patient outcomes.
Incorporating the Latest Research and Advancements
CPR guidelines regularly include the most recent developments in research and medical discoveries. By staying up-to-date with the recommendations, practitioners can take advantage of the most recent discoveries and advancements in CPR, improving the standard of care given.
Standardizing Training and Education
Following CPR guidelines enables uniform training and instruction. It guarantees that people who learn CPR receive consistent and correct instruction and boosts confidence in using the techniques in an emergency.
Legal and Ethical Considerations
The law in some jurisdictions requires healthcare practitioners to adhere to set standards and procedures. Without good justification, steering away from these rules could have legal repercussions and be viewed as a professional ethical violation.
Continuous Quality Improvement
Following CPR guidelines makes it easier to continue improving the standard of care. Healthcare systems can pinpoint areas for improvement, make any necessary protocol adjustments, and increase the overall efficiency of CPR interventions by reviewing results and feedback.
Now that we have a better understanding, it is critical to follow CPR protocols. People can play a crucial role in saving lives in cardiac emergencies by remaining informed and following these guidelines.
CPR Techniques: Then vs. Now
The criteria for conducting CPR have changed over time because of developments in science and research. Making CPR more efficient and improving the odds of survival for patients experiencing cardiac arrest is the main objective of these modifications. The updates are based on a better understanding of the best methods and the application of new technologies to help rescues.
The latest CPR guidelines were announced by the American Heart Association (AHA) and the International Liaison Committee on Resuscitation (ILCOR). We’ll explore the changes to better understand how performing CPR now differs from how it was done in the past.
Mouth-to-Mouth Rescue Breaths
One important change in CPR guidelines is in the first step of performing it. While in the past, CPR consisted of chest compressions and delivering two rescue breaths, now the main focus is only on chest compressions. Chest compressions proved to be just as effective in the first moments of a cardiac arrest.
Focusing only on chest compressions, without the need for rescue breaths, is proven to be effective enough in the initial stages of cardiac arrest. This makes it easier for bystanders and encourages them to provide CPR when needed.
Don’t Look for a Pulse
When a person collapsed, bystanders in the past were required to search for a pulse. This is excluded from the new guidelines. This means that when a person is unconscious, by default, the bystander should assume that it is due to cardiac arrest and administer CPR immediately.
The reasoning is that a cardiac arrest victim has no time to lose, while there is a low chance of harming someone collapsing for other reasons.
Continue CPR and Don’t Give up
Another significant change is when to stop CPR. In the past, if there were no signs of life, the rescuer was supposed to stop performing CPR at a certain point. Today, people are encouraged to continue doing CPR and not give up.
Many studies found that, in some cases, longer CPR attempts benefit patients. Therefore, you should continue with chest compressions until medical help arrives.
Every break in chest compressions means less blood is getting to the brain, lowering a patient’s chance of survival. Remember, do not give up even if it takes a long time.
ABC vs. CAB
Per the older guidelines, practitioners were supposed to follow the ABC order: clear the airway, then rescue breaths, and the last step was chest compressions. The new guidelines simplify this, meaning that performing chest compressions is the first step and the most important one.
The order is now reversed, so CPR rescuers use the CAB order: chest compressions, followed by airway and rescue breathing. Why? Because pausing with compressions means stopping the blood from flowing to the victim’s head, leaving a window for the victim to crash.
Observe, Hear, and Feel
In the past, people used to listen and feel if the person had any signs of life and determine if they should call an ambulance. Today, people are advised to begin CPR as soon as possible and call for an ambulance the moment they notice a problem.
CPR Depth
AHA’s past recommendations were that the practitioner push one and a half to two inches into the chest. Today’s recommended depth is 1.5 inches (4 cm) for newborns and children and 2.4 inches (5–6 cm) for adults.
CPR Compression Rate
As per older guidelines, 100 compressions per minute were considered enough. With the latest updates, the compression rate is 100 to 120 compressions per minute for all age groups.
Who Changes the CPR Guidelines?
Organizations like the American Heart Association (AHA), the European Resuscitation Council (ERC), and the International Liaison Committee on Resuscitation (ILCOR) are responsible for changing CPR guidelines. These organizations have CPR specialists, such as medical professionals, researchers, and scientists, to provide precise and accurate information.
How Frequently Are CPR Guidelines Updated?
CPR guidelines are reviewed and changed every five years to reflect new research and resuscitation techniques. These updates guarantee that the most recent and efficient CPR recommendations are available to healthcare professionals and the general public.
Get Your CPR Plano Certification
Whenever you are ready to obtain a CPR certificate, you can visit the CPR Plano Certification website or the offices closest to you. A CPR certification gives you the knowledge and abilities you might need to save a life.
Once you choose the training course, you can register and start your classes. The great thing about CPR Plano is that you will have in-person live training. Having in-person training is important because it prepares you for how to perform CPR in a real situation.
Training classes last about 3 hrs. Once you complete the class, you must complete a skills check and a written test. After passing the test, you will receive a CPR certification card valid for 2 years. This card proves that you have successfully finished your CPR training and have the correct skills and knowledge to perform CPR when needed.
Final Thoughts
CPR techniques and guidelines will continue to evolve and change. For your knowledge to be current and accurate, you should take recertification classes. Renewal courses, on the other hand, allow you to refresh your memory and learn about any new changes and protocols. You can keep up with changes by following CPR Plano and being aware of them as they occur.
By consistently improving your CPR skills, you develop into a competent responder prepared to positively impact your community when it matters most. You can easily adapt to any adjustments made to techniques or guidelines by staying current with the latest CPR developments.